

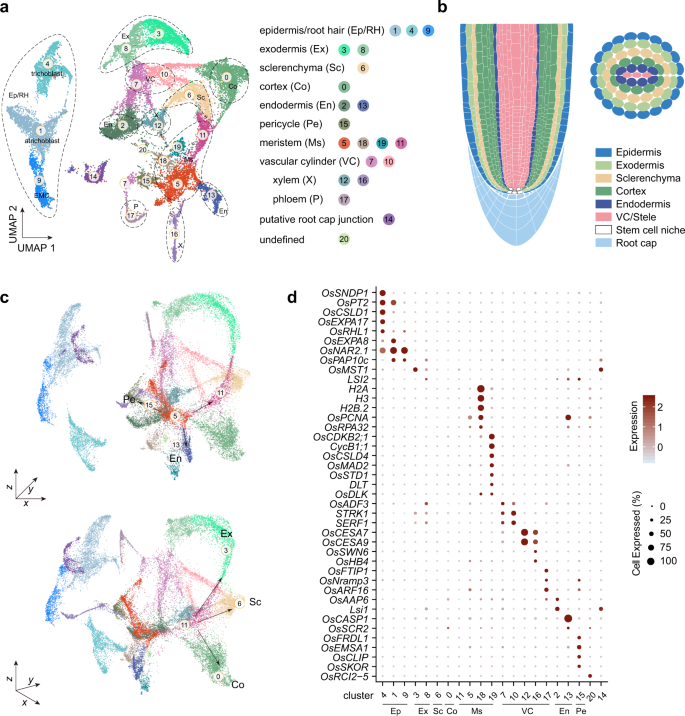
A multi-atlas technique was used to segment and co-register each image. LV short-axis cine images were acquired in 138 healthy volunteers using standard 2D imaging and 3D high spatial resolution CMR. Here we test whether automated cardiac phenotyping using high spatial resolution CMR atlases can achieve improved precision for mapping wall thickness in healthy populations and whether smaller sample sizes are required compared to conventional methods. However this technique is insensitive to the regional variations in wall thickness which are often associated with left ventricular hypertrophy and require large cohorts to reach significance. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have relied on conventional 2D cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) as the gold-standard for phenotyping. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.Cardiac phenotypes, such as left ventricular (LV) mass, demonstrate high heritability although most genes associated with these complex traits remain unidentified. The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not. D'Alessandro, M.D.Īnatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. "Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.Īll contents copyright © 1995-2021 the Author(s) and Michael P. Awards, Reviews, and Comments BookĪnatomy Atlases is curated by Michael P. They have appeared repeatedly for over four hundred years, and have been cataloged.

Nerves, all other organs, and the skeleton. In anatomy, many medically significant, may be found in the muscles, blood supply, Must be remembered that no two bodies are anatomically identical. Provide illustrations that are representations of the human body. This atlas of anatomy, and all other atlases and books depicting human anatomy,
The lymphatic system on the right and left sides of the body.
Plate 22: Lymph vessels and lymph nodes and.Plate 21: Arteries of the pelvis, thigh, leg.Plate 20: Veins of the arm, forearm and hand,.Plate 19: Blood vessels of the neck, thorax,.Plate 18: Arteries of the upper limb, torso.Plate 17a: Arteries of the head, neck and.Plate 17: Blood vessels of the neck and head.Plate 15: Muscles of the dorsal and medial.Plate 14: Muscles of the anterior and lateral.Plate 13: Muscles of the abdomen, pelvis, and.Plate 12: Muscles of the torso and arms.Plate 11: Muscles of the face, trunk, arms,.Plate 10: Muscles of palate, jaw, neck, and.Plate 8: Ligaments of the vertebral column,.Plate 7: Ligaments of the head, vertebral column,.Peer Review Status: Internally Peer Reviewed Carl Ernest Bock, who lived from 1809-1874. The author of this atlas was Professor Dr. This atlas is translated from the original atlas entitled "Handbuch der Anatomie des Menschen" which was published in 1841 in Leipzig, Germany. Anatomy Atlases: Atlas of Human Anatomy - Anatomy | Radiology Anatomy | Anatomy Atlas Atlas of Human Anatomyĭepartments of Pediatrics, Anatomy and Cell Biology, and Neurology


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
